Home » Archives for November 2012

Custom Search
Popular Posts
-
Bursae act as friction-reducing cushions around joints. Inflammation of a bursa, called bursitis, may occur if it is put under prolonged or ...
-
Infection of the testis and epididymis (the coiled tube that stores and transports sperm away from the testis) can lead to inflammation call...
-
If large areas of both sides of the brain or the brainstem are damaged, coma may result. In persistent vegetative state, the parts of the br...
-
Every women differs and so differs there choice of foreplay, some love it to be soft and tender while others relish wild foreplay. Kissing i...
-
A ganglion is a cyst that develops under the skin near a joint and is filled with a jelly-like fluid. The ganglion is usually an outgrowth f...
-
Normally, vaginal bleeding occurs only during a period. Bleeding that occurs outside of menstruation is abnormal. In women under the age o...
-
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is a rare disorder of the brain, causing dementia, abnormal eye movements, and an abnormal gait. The condition d...
Random posts
Blog Archive
Osteomalacia and Rickets
The minerals calcium and phosphate give bone its strength and density. A deficiency of vitamin D results in poor absorption of calcium from the diet, leading to weak and soft bones that are easily deformed or fractured. In adults, the condition is called osteomalacia; in children, it is known as rickets.
What are the causes?
Healthy people obtain the vitanmin D they need partly from their diet (from eggs, fish, green vegetables, fortified margarine, and milk) and partly from vitamin D production in the skin on exposure to sunlight. A deficiency of vitamin D, therefore, is most common in people who eat a restricted diet and receive little direct sunlight. In tropical countries, vitamin D deficiency is almost unknown, except in women who are required to cover their entire bodies. At higher latitudes, deficiency may occur in elderly, housebound people.
Some people cannot absorb vitamin D from food due to intestinal surgery or coeliac diseases. Less commonly, osteomalacia and rickets may be caused by inherited disorders of vitamin D metabolism or chronic kidney failure. In rare cases, drugs used to treat epilepsy interfere with vitamin D metabolism and cause osteomalacia or rickets.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of osteomalacia develop over months or years and may include:
- Painful, tender bones, most often the ribs,hips, and bones of the legs.
- Difficulty in climbing stairs or in getting up from a squatting position.
- Bone fractures after a minor injury.
A child with rickets may experience similar symptoms, and may also have:
- Retarded growth.
- Swelling and tenderness at the growing ends of the bones.
- Prominence of the ribs where they join the breastbone.
Left untreated, bow legs or knock-knees may develop in affected children.
What might be done?
Your doctor may suspect osteomalacia or rickets from your symptoms and a physical examination. He or she may arrange for blood tests to check for low levels of calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D. A bone biopsy, in which a bone sample is taken for analysis, or X-rays can confirm the diagnosis.
If you have a vitamin D deficiency, you should eat foods rich in vitamin D and increase your exposure to sunlight. If you have a disorder that prevents absorption of the vitamin from food, you may need to have vitamin D injections. Calcium supplements may also be required.
After treatment, most people make a full recovery, although deformities that occur in childhood may be permanent.
Read more…
.jpg) |
| Normal And Osteomalacia. |
What are the causes?
Healthy people obtain the vitanmin D they need partly from their diet (from eggs, fish, green vegetables, fortified margarine, and milk) and partly from vitamin D production in the skin on exposure to sunlight. A deficiency of vitamin D, therefore, is most common in people who eat a restricted diet and receive little direct sunlight. In tropical countries, vitamin D deficiency is almost unknown, except in women who are required to cover their entire bodies. At higher latitudes, deficiency may occur in elderly, housebound people.
Some people cannot absorb vitamin D from food due to intestinal surgery or coeliac diseases. Less commonly, osteomalacia and rickets may be caused by inherited disorders of vitamin D metabolism or chronic kidney failure. In rare cases, drugs used to treat epilepsy interfere with vitamin D metabolism and cause osteomalacia or rickets.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of osteomalacia develop over months or years and may include:
- Painful, tender bones, most often the ribs,hips, and bones of the legs.
- Difficulty in climbing stairs or in getting up from a squatting position.
- Bone fractures after a minor injury.
A child with rickets may experience similar symptoms, and may also have:
- Retarded growth.
- Swelling and tenderness at the growing ends of the bones.
- Prominence of the ribs where they join the breastbone.
Left untreated, bow legs or knock-knees may develop in affected children.
What might be done?
Your doctor may suspect osteomalacia or rickets from your symptoms and a physical examination. He or she may arrange for blood tests to check for low levels of calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D. A bone biopsy, in which a bone sample is taken for analysis, or X-rays can confirm the diagnosis.
If you have a vitamin D deficiency, you should eat foods rich in vitamin D and increase your exposure to sunlight. If you have a disorder that prevents absorption of the vitamin from food, you may need to have vitamin D injections. Calcium supplements may also be required.
After treatment, most people make a full recovery, although deformities that occur in childhood may be permanent.
(Admin)
Paget’s disease of the bone
In a healthy person, bone is continually being broken down and replaced by new bone to maintain the normal bone structure. However, in Paget’s disease of the bone (also known as osteitis deformans), the processes involved in the normal breakdown and replacement of bone tissue become disrupted in some parts of the skeleton. The condition may affect any bone in the body, but the pelvis, collarbone, vertebrae (bones of the spine), skull, and leg bones are those most commonly involved. The affected bones become larger and structurally abnormal, which progressively weakens them and makes them more liable to fracture.
Paget’s disease usually develops after the age of 50 and affects 1 in 10 people over the age of 80. The disorder tends to run in families and affects more men than women. Paget’s disease is most common in Europe, North American, and Australia. It is rare in people of Asian and African origin.
What are the symptoms?
Frequently, Paget’s disease produces no symptoms and may be diagnosed only by chance when an X-ray has been taken for some other reason. If symptoms are present, they may include:
- Bone pain that is worse at night.
- Joint pain, especially in those joints near affected bones.
- Bone deformities, such as bow legs or enlargement of the skull.
Long-standing Paget’s disease may also lead to the following complications:
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area if the bone presses on adjacent nervers.
- Hearing loss if abnormal growth of bone compresses nerves to the ear.
In rare cases, a further complication of Paget’s disease is the development of a type of bone cancer.
What may be done?
If your doctor suspects you have Paget’s disease, he or she may arrange for you to have X-ray to confirm the diagnosis. You may also have blood and urine tests to check for abnormal levels of substances involved in the formation and breakdown, of bone. If your hearing is affected, you will probably have hearing tests.
Treatment is not necessary if you have pain or other symptoms and are unlikely to be at risk of fractures. If you are in discomfort, your doctor will prescribe painkillers or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. If these drugs are inadequate then specific treatment may be needed.
The most common treatment is with bisphosphonates; less commonly, the hormone calcitonin may be prescribed. Your response to these drugs may be monitored by blood tests.
Although drug treatment will not reverse any bone deformity that may have already developed. It will slow the progress of the disease.
Read more…
Paget’s disease usually develops after the age of 50 and affects 1 in 10 people over the age of 80. The disorder tends to run in families and affects more men than women. Paget’s disease is most common in Europe, North American, and Australia. It is rare in people of Asian and African origin.
What are the symptoms?
Frequently, Paget’s disease produces no symptoms and may be diagnosed only by chance when an X-ray has been taken for some other reason. If symptoms are present, they may include:
- Bone pain that is worse at night.
- Joint pain, especially in those joints near affected bones.
- Bone deformities, such as bow legs or enlargement of the skull.
Long-standing Paget’s disease may also lead to the following complications:
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area if the bone presses on adjacent nervers.
- Hearing loss if abnormal growth of bone compresses nerves to the ear.
In rare cases, a further complication of Paget’s disease is the development of a type of bone cancer.
What may be done?
If your doctor suspects you have Paget’s disease, he or she may arrange for you to have X-ray to confirm the diagnosis. You may also have blood and urine tests to check for abnormal levels of substances involved in the formation and breakdown, of bone. If your hearing is affected, you will probably have hearing tests.
Treatment is not necessary if you have pain or other symptoms and are unlikely to be at risk of fractures. If you are in discomfort, your doctor will prescribe painkillers or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. If these drugs are inadequate then specific treatment may be needed.
The most common treatment is with bisphosphonates; less commonly, the hormone calcitonin may be prescribed. Your response to these drugs may be monitored by blood tests.
Although drug treatment will not reverse any bone deformity that may have already developed. It will slow the progress of the disease.
Osteoporosis
As people get older, their bones become thinner and lighter. By the age of 70, most people’s skeletons are about a third lighter than they were at the age of 40. This loss of bone density, known as osteoporosis, is the result of an imbalance between the natural breakdown and replaccement of bone. Eventually, all elderly people are affected by osteo-porosis, but the severity of the condition varies from person to person. People who are thin, who do little exercise, and whose relatives have condition to a greater degree than others.
Many people do not realize that they have osteoporosis until their fracture a wrist or hip as a result of a minor fall. In the UK, an estimated 60.000 fractures occur each year in people aged 65 or over. Osteoporosis is a major cause of these fractures, the hip being the most common site. In elderly people, hip fractures are offen life-threating or result in im-mobility.
What are the cause?
Sex hormones are necessary for bone replacement. In both men and women, osteoporosis begins to develop as sex hormone producion declines with age. Any condition that causes this decline to accelerate can increase the severity of age-related osteoporosis. In women, production of the sex hormone oestrogen declines rapidly at the menopause. Early menopause, which tends to occur in women who smoke, increases the risk of osteoporosis. In men, untreated hypogonadism results in low levels of the sex hormone testosterone early in life and a low bone density.
Osteoporosis may occur as a result of long-term treatment with oral cortico-steroids. People with rheuma-toid arthiritis, an overactive thyroid gland, or chronic kidney failure are also at increased risk of osteoporosis.
Exercise is essential to maintain bone health. The density of bones declines rapidly in people who are confined to bed and in those whose daily activity is reduced by disorders such as arthritis or multiple sclerosis.
Osteoporosis sometimes runs in families. Women who have a close relative with oteoporosis are more likely to develop the disoder them-selves.
Can it be prevented?
Measures to prevent osteoporosis are most affective if started early in life. Teenagers and young adults should eat a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D and maintain it throught life. Calcium is essential for bone strength, and vitamin D aids calcium absorption in the body. Extra calcium is needed during pregnancy, while breast-feeding, and during and after the menopause; it may be advisable to take a supplement at such times. Vitamin D is also produced in the skin in respone to sunlight. People exposed to little sun-light may need vitamin D supplements.
Walking and other weight-bearing exercise help to increase bone density. Not smoking and limiting alcohol intake also reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Women may be encouraged to use hormone replacement therapy during and affer the menopause, which may help to protect against osteoporosis, but there is no medical consensus on how long it should be continued.
Anyone thought to be at increased risk of osteoporosis, such as having a family history of the disorder, can have his or her bone density measured. Bone density testing is offen used to assess a person’s likelihood of having bone loss and also to monitor people who are taking preventive treatment.
What are the symptoms?
Some physical changes associated with aging are in fact due to osteoporosis. These include:
- Gradual loss of height.
- Rounding of the back.
For many people, the first evidence of osteoporosis is a pain full fracture of a bone after minor stress or injury. An example is sudden, severe back pain due to a compression fracture of the body of a vertebra (bone of the spine). In severe osteoporosis, a fracture may occur spontaneously.
What might be done?
The diagnosis will be made from your medical history and an examination. Bone densitometry, X-rays, and blood tests may also be performed to exclude other causes of the symptoms, such as osteomalacia and Paget’s disease of the bone, and to look for various disorders that may cause osteoporosis, such as hyperthyroidism.
If you have back pain due to a fracture, your doctor may recommend that you take painkillers or use a heat pad. Underlying disorders will be treated if possible. For example, you may be prescribed drugs to treat an overactive thyroid gland.
To slow the progression of osteoporosis, it is important to follow the advice given above for taking preventive measures. Most drugs simply slow the rate of bone loss, although there is evidence that bisphosphonates reduce the risk of fractures. However, even if these measures are taken, some bone loss is inevitable in later life.
TEST BONE DENSITOMETRY:
This technique uses low-dose X-rays to measure the density of bone. The test is carried out to screen for and diagnose osteoporosis, a condition that is particularly common in post-menopausal women. The varying absorption of X-rays as they pass computer and displayed as an image. The computer calculates the average density of the bone and compares it with the normal range for the person’s age and sex. The procedure takes about 10-20 minutes and is painless.
Read more…
Many people do not realize that they have osteoporosis until their fracture a wrist or hip as a result of a minor fall. In the UK, an estimated 60.000 fractures occur each year in people aged 65 or over. Osteoporosis is a major cause of these fractures, the hip being the most common site. In elderly people, hip fractures are offen life-threating or result in im-mobility.
 |
| Normal And Osteoporosis. |
What are the cause?
Sex hormones are necessary for bone replacement. In both men and women, osteoporosis begins to develop as sex hormone producion declines with age. Any condition that causes this decline to accelerate can increase the severity of age-related osteoporosis. In women, production of the sex hormone oestrogen declines rapidly at the menopause. Early menopause, which tends to occur in women who smoke, increases the risk of osteoporosis. In men, untreated hypogonadism results in low levels of the sex hormone testosterone early in life and a low bone density.
Osteoporosis may occur as a result of long-term treatment with oral cortico-steroids. People with rheuma-toid arthiritis, an overactive thyroid gland, or chronic kidney failure are also at increased risk of osteoporosis.
Exercise is essential to maintain bone health. The density of bones declines rapidly in people who are confined to bed and in those whose daily activity is reduced by disorders such as arthritis or multiple sclerosis.
Osteoporosis sometimes runs in families. Women who have a close relative with oteoporosis are more likely to develop the disoder them-selves.
Can it be prevented?
Measures to prevent osteoporosis are most affective if started early in life. Teenagers and young adults should eat a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D and maintain it throught life. Calcium is essential for bone strength, and vitamin D aids calcium absorption in the body. Extra calcium is needed during pregnancy, while breast-feeding, and during and after the menopause; it may be advisable to take a supplement at such times. Vitamin D is also produced in the skin in respone to sunlight. People exposed to little sun-light may need vitamin D supplements.
Women may be encouraged to use hormone replacement therapy during and affer the menopause, which may help to protect against osteoporosis, but there is no medical consensus on how long it should be continued.
Anyone thought to be at increased risk of osteoporosis, such as having a family history of the disorder, can have his or her bone density measured. Bone density testing is offen used to assess a person’s likelihood of having bone loss and also to monitor people who are taking preventive treatment.
What are the symptoms?
Some physical changes associated with aging are in fact due to osteoporosis. These include:
- Gradual loss of height.
- Rounding of the back.
For many people, the first evidence of osteoporosis is a pain full fracture of a bone after minor stress or injury. An example is sudden, severe back pain due to a compression fracture of the body of a vertebra (bone of the spine). In severe osteoporosis, a fracture may occur spontaneously.
What might be done?
The diagnosis will be made from your medical history and an examination. Bone densitometry, X-rays, and blood tests may also be performed to exclude other causes of the symptoms, such as osteomalacia and Paget’s disease of the bone, and to look for various disorders that may cause osteoporosis, such as hyperthyroidism.
If you have back pain due to a fracture, your doctor may recommend that you take painkillers or use a heat pad. Underlying disorders will be treated if possible. For example, you may be prescribed drugs to treat an overactive thyroid gland.
To slow the progression of osteoporosis, it is important to follow the advice given above for taking preventive measures. Most drugs simply slow the rate of bone loss, although there is evidence that bisphosphonates reduce the risk of fractures. However, even if these measures are taken, some bone loss is inevitable in later life.
TEST BONE DENSITOMETRY:
This technique uses low-dose X-rays to measure the density of bone. The test is carried out to screen for and diagnose osteoporosis, a condition that is particularly common in post-menopausal women. The varying absorption of X-rays as they pass computer and displayed as an image. The computer calculates the average density of the bone and compares it with the normal range for the person’s age and sex. The procedure takes about 10-20 minutes and is painless.
(Admin)
Yoga _What You Need to Know Before Starting Yoga
Is yoga something that interests you, but you feel a bit intimidated? I know I felt that yoga was only for very flexible people and I’m not very flexible. all you see in yoga ads are people in gravity-defying positions or people who can wrap their legs over their heads. Yoga looks like it’s just for contortionists Doesn’t it? well that wasn’t what yoga is about at all.
Yoga has three different levels. the first is physical health. Yoga was used as a means moving a person from the physical world into the spiritual world and was a prep for meditation. Have you ever meditated for long periods of time? it sounds fun and relaxing? well if you sit in a meditation pose for longer than 20-30 minutes, if you started sitting for hours, if you’re not physically fit it really starts to hurt. the second is mental and emotional health. Yoga is excellent for improving your memory and concentration, releasing stress and tension and can even help with depression and anxiety the third is spiritual – most people don’t practice yoga for spiritual reasons and you can practice yoga without this component but benefits such as self-awareness. Yoga means to yolk or join and ancient indian practitioners believed that the two energy centers called Ha and Tha could be combined using Yoga. Yoga also seems to evoke altruism and compassion. the feeling of being one with other beings on the planet, with nature and the environment, these are all linked to a yoga practice.
Why are more and more people are becoming interested in yoga
So why are more people becoming interested in yoga? here are my theories: the aging population in developed countries are looking for a better way to get fit. They are turning away from high impact exercises which can strain muscles and cause injuries and looking for low impact activities such as Pilates and Yoga, which gives results of increased muscle tone without as much cause for injury and damage.
What equipment will you need?
Here are a few basic bits of equipment that you may or may not need. You can spend quite a bit of money so make sure that you buy only what you need. Yoga studios will also supply equipment that you don’t have, so don’t rush out and buy these all at once. Yoga props include: a yoga mat yoga clothes (comfortable clothes) yoga props such as a yoga bolster, yoga meditation pillow and strap (this is if you choose to do Iyengar yoga).
Do you need specialized yoga clothes?
It depends, on what type of yoga you’re doing low impact such as Viniyoga, Kundalini, Anahat just needs loose clothing but for more athletic yoga styles (Bikram, Ashtanga, Vinyasa Flow), breathable materials such as cotton and neoprene.
Importance of Daily Practice: why it is important to do yoga everyday
Similar to martial arts, you get a deeper knowledge or understanding of yoga by practicing on your own at home. an example of this is when a teacher gives you a lecture. if you don’t look over the material, you won’t remember it as well and you’ll forget the important points of the information.
What to look for in a yoga class and a yoga teacher
Look into a class before starting yoga. Find out what the teacher is like. Do you like the vibe of the classroom? does it work for you? Is it a good fit? How much experience does this teacher have with teaching others? Do I feel that the teacher understands and addresses my needs? does the class meet my needs and expectations? Is the studio or environment a good fit for me?
What to do before Class: Getting yourself ready for yoga class
Once you’ve settled for a yoga class that’s right for you and have come to your very first class. Here’s a checklist of things you need to bring make sure to bring a change of clothes (especially for Bikram or Moksha Yoga), make sure that you’ve brought the right equipment (even if it’s just a bottle of water). And don’t forget to wash your feet Remember not to eat a couple of hours before hand and make sure to go to the bathroom before settling in class. this is because some of the poses will put pressure on your inner organs and eating makes you feel really uncomfortable in these positions (trust me I’ve done it and it feels terrible)
Remember, going to a Yoga class or doing Yoga at home shouldn’t be intimidating. You should feel great after every class. Enjoy.
Read more…
Yoga has three different levels. the first is physical health. Yoga was used as a means moving a person from the physical world into the spiritual world and was a prep for meditation. Have you ever meditated for long periods of time? it sounds fun and relaxing? well if you sit in a meditation pose for longer than 20-30 minutes, if you started sitting for hours, if you’re not physically fit it really starts to hurt. the second is mental and emotional health. Yoga is excellent for improving your memory and concentration, releasing stress and tension and can even help with depression and anxiety the third is spiritual – most people don’t practice yoga for spiritual reasons and you can practice yoga without this component but benefits such as self-awareness. Yoga means to yolk or join and ancient indian practitioners believed that the two energy centers called Ha and Tha could be combined using Yoga. Yoga also seems to evoke altruism and compassion. the feeling of being one with other beings on the planet, with nature and the environment, these are all linked to a yoga practice.
Why are more and more people are becoming interested in yoga
So why are more people becoming interested in yoga? here are my theories: the aging population in developed countries are looking for a better way to get fit. They are turning away from high impact exercises which can strain muscles and cause injuries and looking for low impact activities such as Pilates and Yoga, which gives results of increased muscle tone without as much cause for injury and damage.
What equipment will you need?
Here are a few basic bits of equipment that you may or may not need. You can spend quite a bit of money so make sure that you buy only what you need. Yoga studios will also supply equipment that you don’t have, so don’t rush out and buy these all at once. Yoga props include: a yoga mat yoga clothes (comfortable clothes) yoga props such as a yoga bolster, yoga meditation pillow and strap (this is if you choose to do Iyengar yoga).
Do you need specialized yoga clothes?
It depends, on what type of yoga you’re doing low impact such as Viniyoga, Kundalini, Anahat just needs loose clothing but for more athletic yoga styles (Bikram, Ashtanga, Vinyasa Flow), breathable materials such as cotton and neoprene.
Importance of Daily Practice: why it is important to do yoga everyday
Similar to martial arts, you get a deeper knowledge or understanding of yoga by practicing on your own at home. an example of this is when a teacher gives you a lecture. if you don’t look over the material, you won’t remember it as well and you’ll forget the important points of the information.
What to look for in a yoga class and a yoga teacher
Look into a class before starting yoga. Find out what the teacher is like. Do you like the vibe of the classroom? does it work for you? Is it a good fit? How much experience does this teacher have with teaching others? Do I feel that the teacher understands and addresses my needs? does the class meet my needs and expectations? Is the studio or environment a good fit for me?
What to do before Class: Getting yourself ready for yoga class
Once you’ve settled for a yoga class that’s right for you and have come to your very first class. Here’s a checklist of things you need to bring make sure to bring a change of clothes (especially for Bikram or Moksha Yoga), make sure that you’ve brought the right equipment (even if it’s just a bottle of water). And don’t forget to wash your feet Remember not to eat a couple of hours before hand and make sure to go to the bathroom before settling in class. this is because some of the poses will put pressure on your inner organs and eating makes you feel really uncomfortable in these positions (trust me I’ve done it and it feels terrible)
Remember, going to a Yoga class or doing Yoga at home shouldn’t be intimidating. You should feel great after every class. Enjoy.
(healtharticles4free.com)
Art of Lovemaking and Science of Viagra
Every women differs and so differs there choice of foreplay, some love it to be soft and tender while others relish wild foreplay. Kissing is probably the most important part of foreplay or even sex for that matter. It's not just about kissing her mouth; let her feel you all over. Don't let her feel that you are neglecting any part of her body.
Removing her clothes can be a very important part of foreplay. You have two choices: slow or fast. The reason you should try both is because women love variety and to figure out what she really likes can be a fantabulous onset.
It's always good to discuss your feelings while having sex, try to stimulate her imagination; this will help her reach climax. Do not hassle in sharing your likes and dislikes, talk about your problems. If you are facing serious physical disorder like erectile dysfunction.
Keep on experimenting with sex to make it more exciting, try to implement a variety of techniques rather than rather then doing the same thing over and over again. Discuss with your partner whether he or she is enjoying a particular pose or not.
There is no rule and regulation in bed, don't feel embarrassed in trying something new, its all about satisfying yourself and your partner.
If your partner has any problem discuss it, if he is not able to sustain erection console him and suggest him prescription pill Viagra. Viagra helps in maintaining erection and enhancing sexual duration.
Thanks to medical sciences that has provided successful, effectual and easy solution to erectile dysfunction. You don't need to go for the painful as well as embarrassing surgery. The onset of Viagra is amazingly fast and the effect lasts for around 4 hours giving enough time to plan out and enjoy the sexual desires.
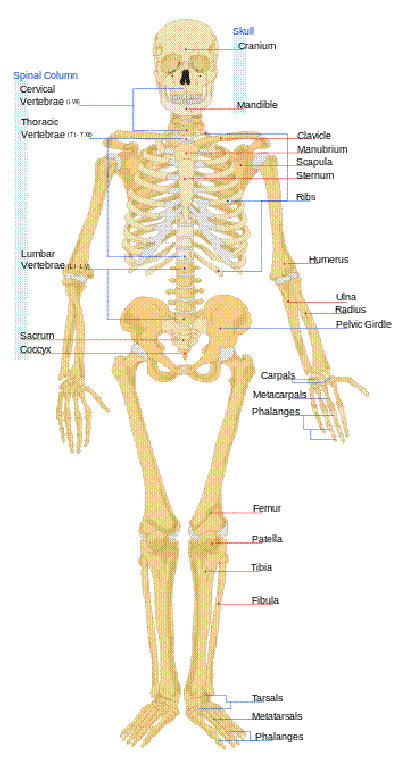
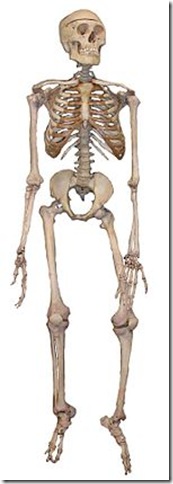
Human skeleton
Human newborns have over 270 bones[1][2][3] some of which fuse together into a longitudinal axis, the axial skeleton, to which the appendicular skeleton is attached.[4]
Contents
1 Axial skeleton
2 Appendicular skeleton
3 Function
3.1 Support
3.2 Movement
3.3 Protection
3.4 Blood cell production
3.5 Storage
3.6 Endocrine regulation
4 Sexual dimorphism
5 Disorders
5.1 Osteoporosis
6 References
1. Axial skeleton:
The axial skeleton (80 bones) is formed by the vertebral column (26), the rib cage (12 pairs of ribs and the sternum), and the skull (22 bones and 7 associated bones). The upright posture of humans is maintained by the axial skeleton, which transmits the weight from the head, the trunk, and the upper extremities down to the lower extremities at the hip joints. The bones of the spine are supported by many ligaments. The erectors spinae muscles are also supporting and are useful for balance.
2. Appendicular skeleton:
The appendicular skeleton (126 bones) is formed by the pectoral girdles (4), the upper limbs (60), the pelvic girdle (2), and the lower limbs (60). Their functions are to make locomotion possible and to protect the major organs of locomotion, digestion, excretion, and reproduction.
3. Function:
The skeleton serves six major functions.
Support
The skeleton provides the framework which supports the body and maintains its shape. The pelvis, associated ligaments and muscles provide a floor for the pelvic structures. Without the rib cages, costal cartilages, and intercostal muscles, the heart would collapse.
Movement
The joints between bones permit movement, some allowing a wider range of movement than others, e.g. the ball and socket joint allows a greater range of movement than the pivot joint at the neck. Movement is powered by skeletal muscles, which are attached to the skeleton at various sites on bones. Muscles, bones, and joints provide the principal mechanics for movement, all coordinated by the nervous system.
Protection
The skeleton protects many vital organs:
- The skull protects the brain, the eyes, and the middle and inner ears.
- The vertebrae protect the spinal cord.
- The rib cage, spine, and sternum protect the human lungs, human heart and major blood vessels.
- The clavicle and scapula protect the shoulder.
- The ilium and spine protect the digestive and urogenital systems and the hip.
- The patella and the ulna protect the knee and the elbow respectively.
- The carpals and tarsals protect the wrist and ankle respectively.
Blood cell production
The skeleton is the site of haematopoiesis, the development of blood cells that takes place in the bone marrow.
Storage
Bone matrix can store calcium and is involved in calcium metabolism, and bone marrow can store iron in ferrotin and is involved in iron metabolism. However, bones are not entirely made of calcium, but a mixture of chondroitin sulfate and hydroxyapatite, the latter making up 70% of a bone.
Endocrine regulation
Bone cells release a hormone called osteocalcin, which contributes to the regulation of blood sugar (glucose) and fat deposition. Osteocalcin increases both the insulin secretion and sensitivity, in addition to boosting the number of insulin-producing cells and reducing stores of fat.[5]
4. Sexual dimorphism:
An articulated human skeleton, as used in biology education
There are many differences between the male and female human skeletons. Most prominent is the difference in the pelvis, owing to characteristics required for the processes of childbirth. The shape of a female pelvis is flatter, more rounded and proportionally larger to allow the head of a fetus to pass. A male's pelvis is about 90 degrees or less of angle, whereas a female's is 100 degrees or more. Also, the coccyx of a female's pelvis is oriented more inferiorly whereas a male's coccyx is usually oriented more anteriorly. This difference allows more room for childbirth. Males tend to have slightly thicker and longer limbs and digit bones (phalanges), while females tend to have narrower rib cages, smaller teeth, less angular mandibles, less pronounced cranial features such as the brow ridges and external occipital protuberance (the small bump at the back of the skull), and the carrying angle of the forearm is more pronounced in females. Females also tend to have more rounded shoulder blades.
5. Disorders:
There are many classified skeletal disorders. One of the most common is osteoporosis. Also common is scoliosis, a side-to-side curve in the back or spine, often creating a pronounced "C" or "S" shape when viewed on an x-ray of the spine. This condition is most apparent during adolescence, and is most common with females.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bone, which leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis, the bone mineral density (BMD) is reduced, bone microarchitecture is disrupted, and the amount and variety of non-collagenous proteins in bone is altered. Osteoporosis is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in women as a bone mineral density 2.5 standard deviations below peak bone mass (20-year-old sex-matched healthy person average) as measured by DXA; the term "established osteoporosis" includes the presence of a fragility fracture.[6] Osteoporosis is most common in women after the menopause, when it is called postmenopausal osteoporosis, but may develop in men and premenopausal women in the presence of particular hormonal disorders and other chronic diseases or as a result of smoking and medications, specifically glucocorticoids, when the disease is craned steroid- or glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (SIOP or GIOP).
Osteoporosis can be prevented with lifestyle advice and medication, and preventing falls in people with known or suspected osteoporosis is an established way to prevent fractures. Osteoporosis can also be prevented with having a good source of calcium and vitamin D. Osteoporosis can be treated with bisphosphonates and various other medical treatments.
References:
1. Miller, Larry (2007-12-09). "We're Born With 270 Bones. As Adults We Have 206". Ground Report. http://www.groundreport.com/Health_and_Science/We-re-Born-With-270-Bones-As-Adults-We-Have-206.
2. "How many bones does the human body contain?". Ask.yahoo.com. 2001-08-08. http://ask.yahoo.com/20010808.html. Retrieved 2010-03-04.
3. Exploring our human bodies. San Diego Supercomputer Center Education
4. Tözeren, Aydın (2000). Human Body Dynamics: Classical Mechanics and Human Movement. Springer. pp. 6–10. ISBN 0-387-98801-7.
5. Lee, Na Kyung; et al. (10 August 2007). "Endocrine Regulation of Energy Metabolism by the Skeleton". Cell 130 (3): 456–469. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.047. PMC 2013746. PMID 17693256. http://download.cell.com/pdfs/0092-8674/PIIS0092867407007015.pdf. Retrieved 2008-03-15.
6. WHO (1994). "Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group". World Health Organization technical report series 843: 1–129. PMID 7941614.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_skeleton#Sexual_dimorphism

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)